Find the most interesting financial charts!
Our mission is to find the most interesting and educational charts with rich historical data, and to make these charts available online.
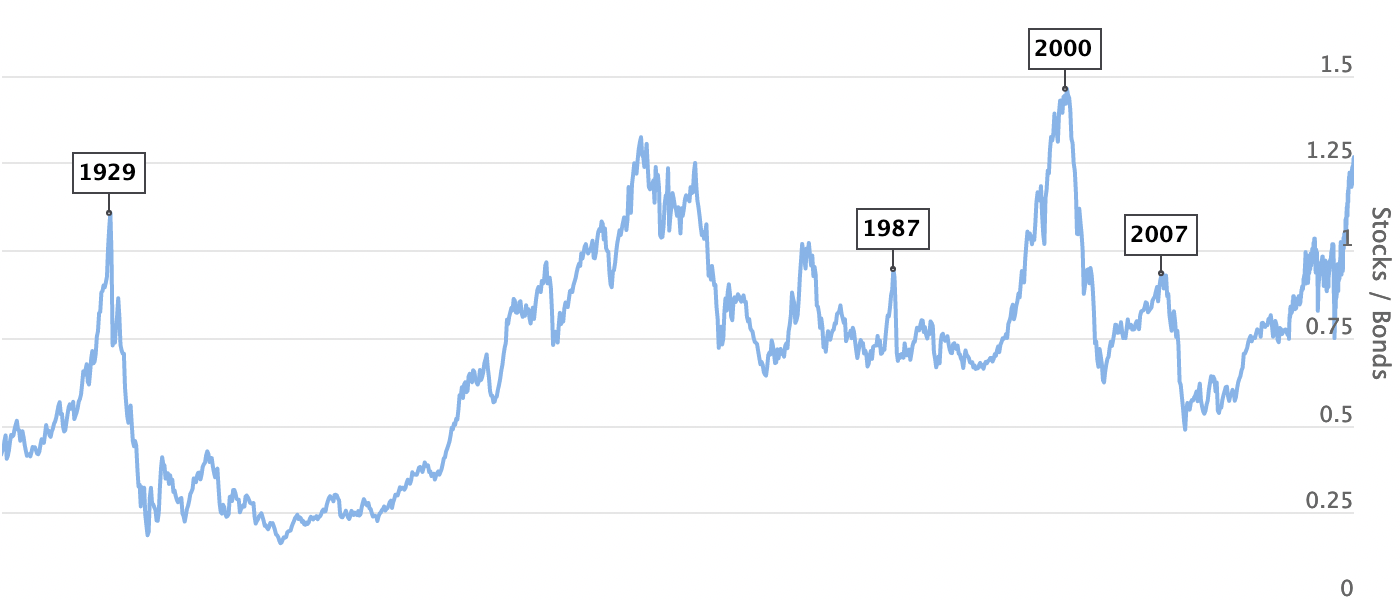
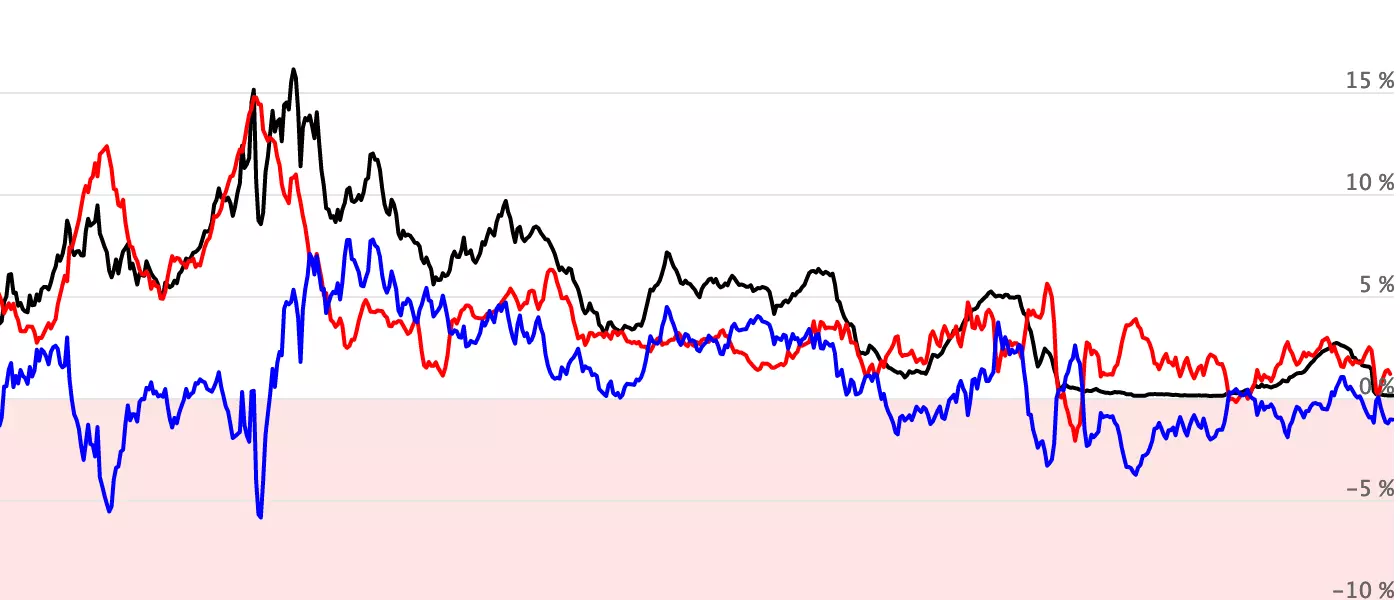
Our mission is to find the most interesting and educational charts with rich historical data, and to make these charts available online.


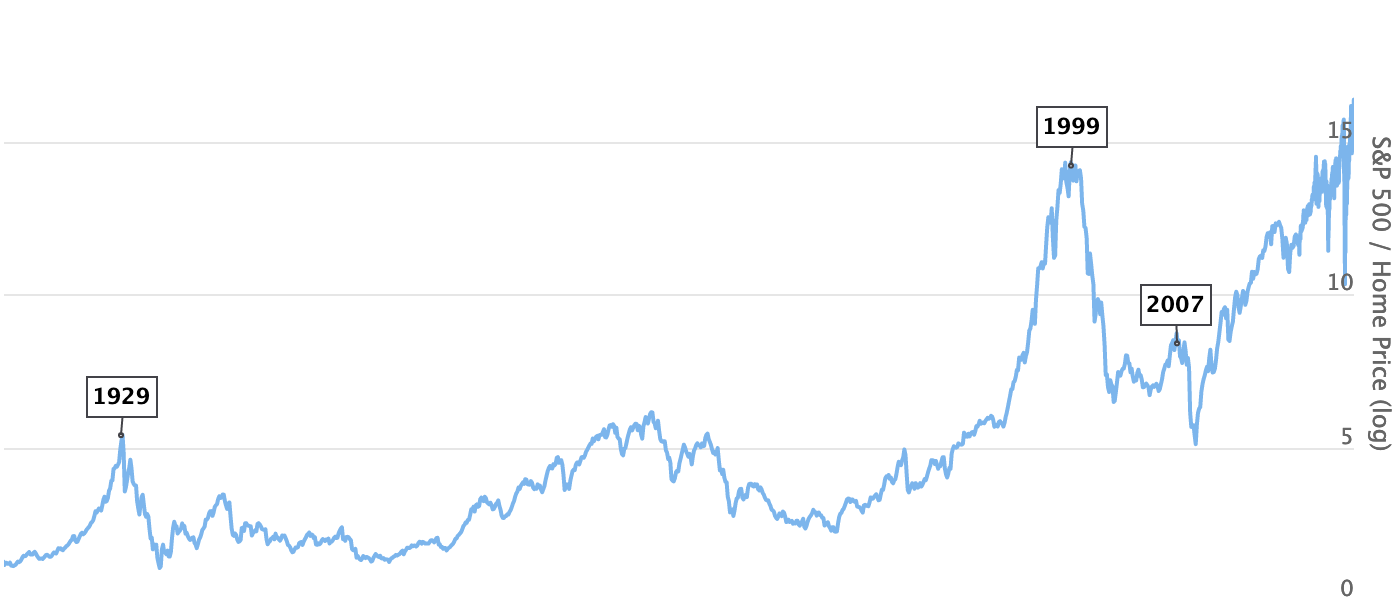
The Stocks to Real Estate ratio divides the S&P 500 index by the Case-Shiller Home Price Index. Just like Market Cap to GDP, it has an interesting historical track record and clearly shows the stock market bubbles of 1929 and 1999.
An error appeared while loading the data. Maybe there is a technical problem with the data source. Please let me know if this happens regularly @silvan_frank.